Incomplete Dominance

In the snapdragon, Antirrhinum majus, a cross between a homozygous white-flowered plant (CWCW) and a homozygous red-flowered plant (CRCR) will produce offspring with pink flowers (CWCR).
This type of relationship between alleles, with a heterozygote phenotype intermediate between the two homozygote phenotypes is incomplete dominance.
Codominance
•Codominance occurs when pairs of alleles are both expressed equally in the phenotype of a heterozygous individual
•Heterozygotes therefore have an altered phenotype as the alleles are having a joint effect
•When representing alleles, the convention is to use superscripts for the different co-dominant alleles (recessive still lower case)
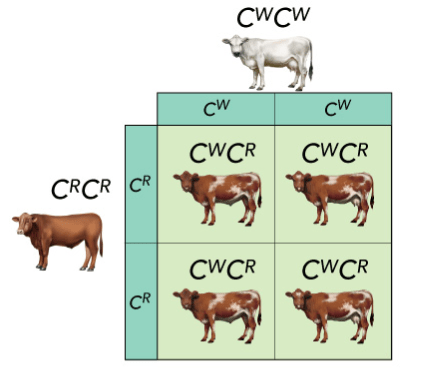
•An example of co-dominance is feathering in chickens – black (CB) and white (CW) feathers create a speckled coat (CBCW).

Codominance in Blood Groups
•Human red blood cells can be categorised into different blood groups based on the structure of a surface glycoprotein (antigen).
•ABO blood groups are controlled by a single gene with multiple alleles (A, B, O).
•The A, B and O alleles all produce a basic antigen on the surface of red blood cells.
•The A and B alleles are codominant and each modify the structure of the antigen to produce different variants.
•The O allele is recessive and does not modify the basic antigenic structure.
•When representing blood group alleles, the letter I is used to represent the different antigenic forms (isoagglutinogen).
•A allele = IA ; B allele = IB ; O allele = i (recessive).